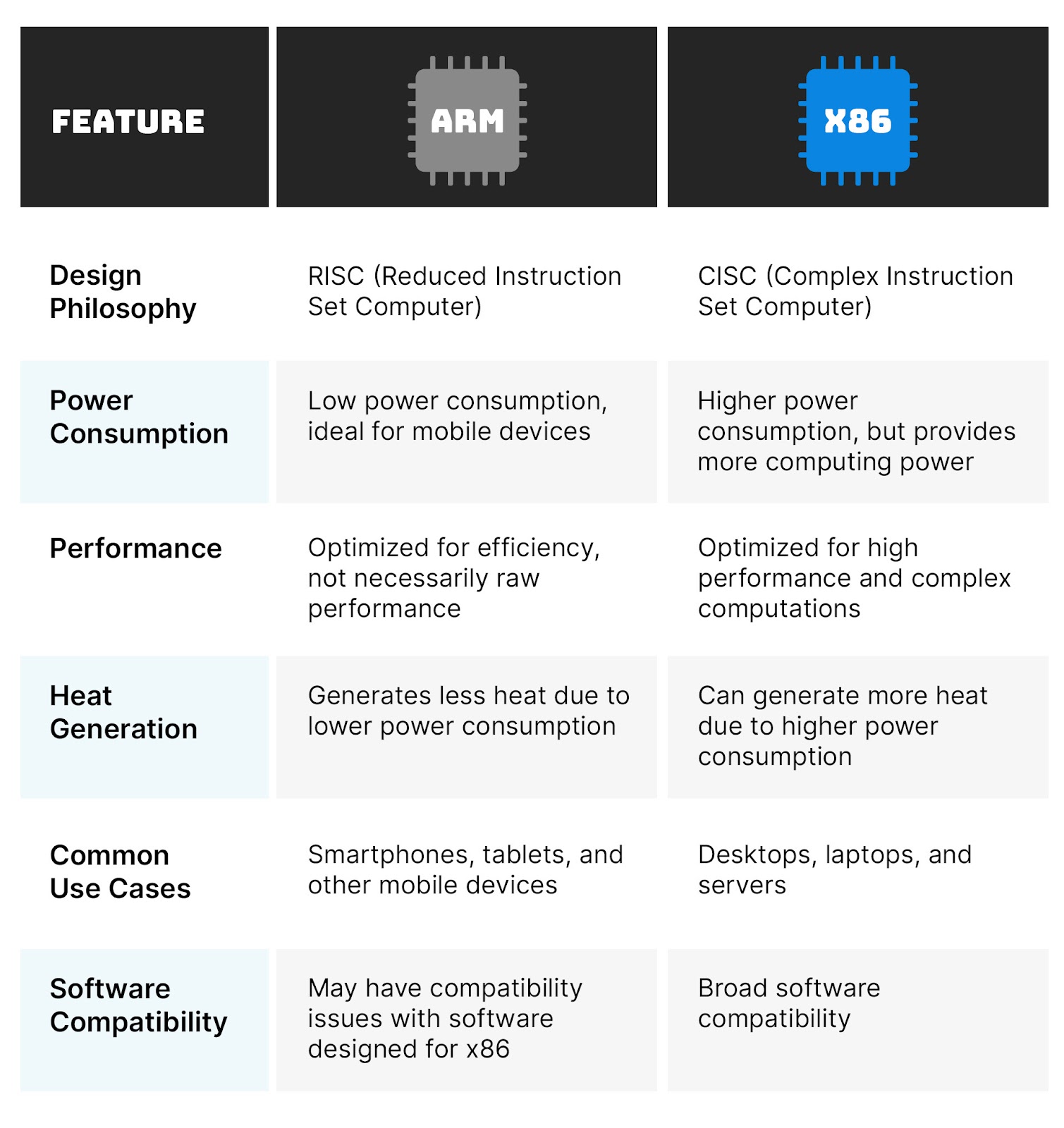
In the digital universe, the processor serves as the heart of a computer, executing instructions from computer programs and enabling a plethora of tasks. Among the myriad of processor types, ARM and x86 emerge as the leading contenders, each boasting unique attributes and applications.
Decoding Processors: The Central Nervous System of Computing
Before we delve into the nuances of ARM and x86 processors, let’s demystify the concept of a processor. A processor, or a microprocessor, is an integrated circuit (IC) that dutifully carries out instructions stored within the computer’s memory. These instructions form the foundation of computer operations, encompassing arithmetic computations, data manipulation, and logical evaluations.
Processors are intricate labyrinths of millions, or even billions, of transistors, minuscule electronic switches that regulate the flow of electricity through the processor’s circuitry. The processor’s speed, measured in gigahertz (GHz), determines its efficiency in executing instructions. Higher clock speeds equate to faster instruction processing.
ARM Processors: Masters of Efficiency and Compactness
They are meticulously engineered to prioritize simplicity and energy efficiency, making them ideal for mobile devices like smartphones and tablets where battery longevity is paramount. ARM, an acronym for Advanced RISC Machine, where RISC signifies Reduced Instruction Set Computer, implies that ARM processors employ a set of streamlined instructions that can be executed within a single clock cycle. This simplicity translates to reduced power consumption, thereby extending the device’s battery life.
ARM processors boast a smaller footprint compared to their x86 counterparts, making them ideal for integration into compact devices. Despite their diminutive size, ARM processors deliver impressive performance, particularly for tasks like web browsing and media playback.
X86 Processors: Powerhouses for Demanding Applications
In contrast, x86 processors are renowned for their complexity and processing prowess. They are the driving force behind devices like desktop computers and laptops, which demand substantial computing power to handle sophisticated software applications. The term “x86” stems from the naming convention of early processors in this family, such as the Intel 8086.
Unlike ARM processors, x86 processors adhere to a Complex Instruction Set Computer (CISC) architecture. This means they employ a vast repertoire of complex instructions, each capable of executing multiple operations simultaneously. This complexity empowers x86 processors to deliver exceptional performance, albeit at the expense of increased power consumption and heat generation compared to ARM processors.
With the introduction of Qualcomm’s Snapdragon X Elite, the landscape is changing. This new ARM-based chip offers comparable performance to x86 processors while maintaining the power efficiency advantages of ARM. This could potentially disrupt the dominance of x86 processors in the laptop market.
Qualcomm’s Game-Changing Chip: Snapdragon X Elite
Apple had introduced ARM-based chips for their MacBooks and iMacs with M series of chips but since it’s manufactured by Apple, they were only available for Apple Computers. The industry and the consumers were waiting for an ARM-based chip for non-apple laptops and PCs.
Qualcomm, a pioneer in ARM processors for mobile devices, recently unveiled the Snapdragon X Elite, a groundbreaking chip designed specifically for laptops. This innovation is poised to revolutionize the market with its transformative capabilities.
The Snapdragon X Elite leverages an advanced manufacturing process, enabling it to surpass the efficiency and performance of previous ARM processor generations. Qualcomm claims that this new chip rivals the performance of the latest Intel x86 processors while consuming significantly less power. This implies that laptops powered by the Snapdragon X Elite could potentially achieve extended battery life without compromising performance.
In addition to its impressive processing prowess, the Snapdragon X Elite boasts exceptional graphics processing capabilities, catering to demanding tasks like gaming and video editing. The Snapdragon X Elite seamlessly supports multiple high-resolution monitors and incorporates specialized features for handling high-quality video files.
The advent of Qualcomm’s Snapdragon X Elite could herald a significant shift in the laptop market. With its impressive balance of performance and power efficiency, this new chip could challenge the dominance of x86 processors in laptops. As technology continues to evolve, it will be intriguing to see how this competition between ARM and x86 processors unfolds. The future of computing is thrilling, and we eagerly anticipate what lies ahead.



No Comments
Leave a comment Cancel